8K Era, Why TV choose AI technology?
Recently, Samsung’s 8K TV has become a shining light in the market. But do you know that Samsung actually uses Artificial Intelligence Technology to upgrade, which is AI’s way to improve image quality, and converts the current mainstream low-resolution video to a higher 4k and 8K resolution that can be played on a TV screen. Samsung has begun adding Artificial Intelligence Technology to its 8K and 4K QLED TVs. Samsung cancelled traditional copper HDMI CABLE from their new 8K TV. Build a customized Multi-functional Active Optical Cable, which can realize real-time, lossless optical speed transmission. OE (Optical to Electronic) converting technology is the expertise of Smartavlink team. Combining HDMI AOC, USB AOC and Type C AOC (Active Optical Cable), you can customize a multi-functional custom fiber optic cables for your private application, but this is not the focus of our discussion today (Below is Samsung customrized optical fiber solution for 8K OLED TV ) : So, how is the Artificial Intelligence Technology of Samsung TV realized?
So, how is the Artificial Intelligence Technology of Samsung TV realized?
To understand AI, you have to learn “ Up-scaling “ firstly.
Almost all current TV products have a fixed number of pixels, or separate image elements, that are fused together to form a complete image. This is their resolution, usually called 1080p, Ultra HD 4K, or now the highest 8K. The TV you are using, if it was bought a few years ago, is likely to be 1080 resolution. Almost all current TV products have a fixed number of pixels, or separate image elements, that are fused together to form a complete image. This is their resolution, usually called 1080p, Ultra HD 4K, or now the highest 8K. The TV you are using, if it was purchased a few years ago, is likely to be 1080 resolution. This means that it is 1920 pixels wide and 1080 pixels vertically. Ultra HD 4K TVs have twice the vertical and horizontal resolution of the above two numbers, 8K is twice the resolution number of 4K.
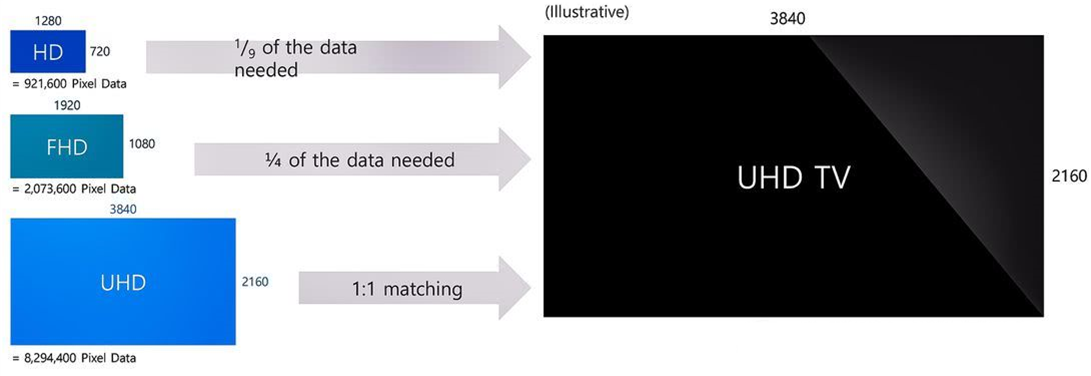
As you can see, non-4K resolution sources, like almost all broadcast and cable TV, have far fewer pixels than the 4K TV itself. If you want the frame to fill the screen, the TV must have its own pixels to display the data. If you play on a 1080p TV with a 1080p resolution Blu-ray disc, there is no problem. The blue light source has as many pixels as the TV, and everything is just right.
But the real challenge is that not all content has the same resolution as the TV resolution. When you play a DVD with a resolution of 720 x 480 on a 1080p TV, the TV must create brand new pixels to fill all areas of the screen. The same is true for 4K TVs when playing 1080p resolution video. Since 4K TVs have twice the horizontal resolution and vertical resolution of ordinary TVs, they require four times as many pixels to produce a full-screen image.

This process of creating new pixels is called up-conversion, up-scaling, or just scaling. They probably have the same meanings, essentially ‘amplifying’ on the basis of low-resolution images, so it can fill higher-resolution screens.
There are many ways to do this at present, but the easiest way is to create extra, identical pixels from each raw pixel. For the conversion from 1080p to 4K, we need to perform 4 times of processing from each original. This process is the process of Up-scaling.
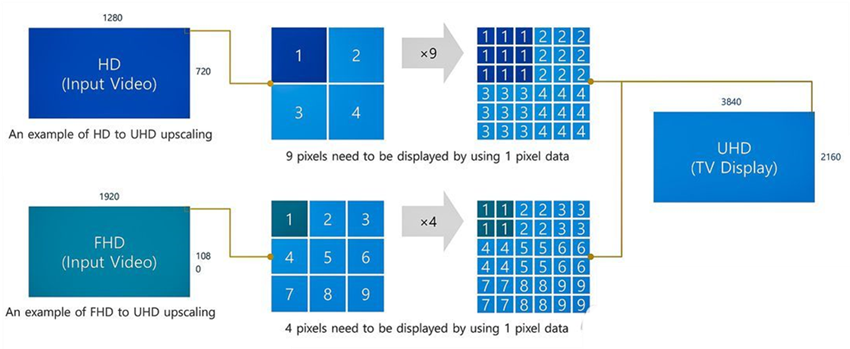 As the speed of TV processors increases, the scaling technology is becoming more and more advanced, and TV companies are looking for other more advanced methods to improve picture quality. Instead of simply converting 1 to 4 pixels, the TV processor determines the color of the new pixel by analyzing the color of the adjacent pixels. This allows the enlarged picture to be clearer, the edges to be clearer, and the details seen by the naked eye. Or in other words, it will make your DVD picture looks less blurry on a 1080p TV with simple scaling.
As the speed of TV processors increases, the scaling technology is becoming more and more advanced, and TV companies are looking for other more advanced methods to improve picture quality. Instead of simply converting 1 to 4 pixels, the TV processor determines the color of the new pixel by analyzing the color of the adjacent pixels. This allows the enlarged picture to be clearer, the edges to be clearer, and the details seen by the naked eye. Or in other words, it will make your DVD picture looks less blurry on a 1080p TV with simple scaling.
Research on processor performance in recent years has not only looked at adjacent pixels in each frame, but also looked for motion, noise and many other factors between multiple frames to create an image with as much detail as possible while maintaining Video noise reduction and other elements. The above explanation is a very simplified process. It turns out that the appropriate sharpness, noise reduction and other factors are the premise and guarantee for the better effect of artificial intelligence.
Usually, TV engineers have their own exclusive secrets when designing, including getting the best images from their company’s latest video processor. The processor will determine which combination of sharpness enhancement, noise reduction, etc., with the enlarged content will look the best.
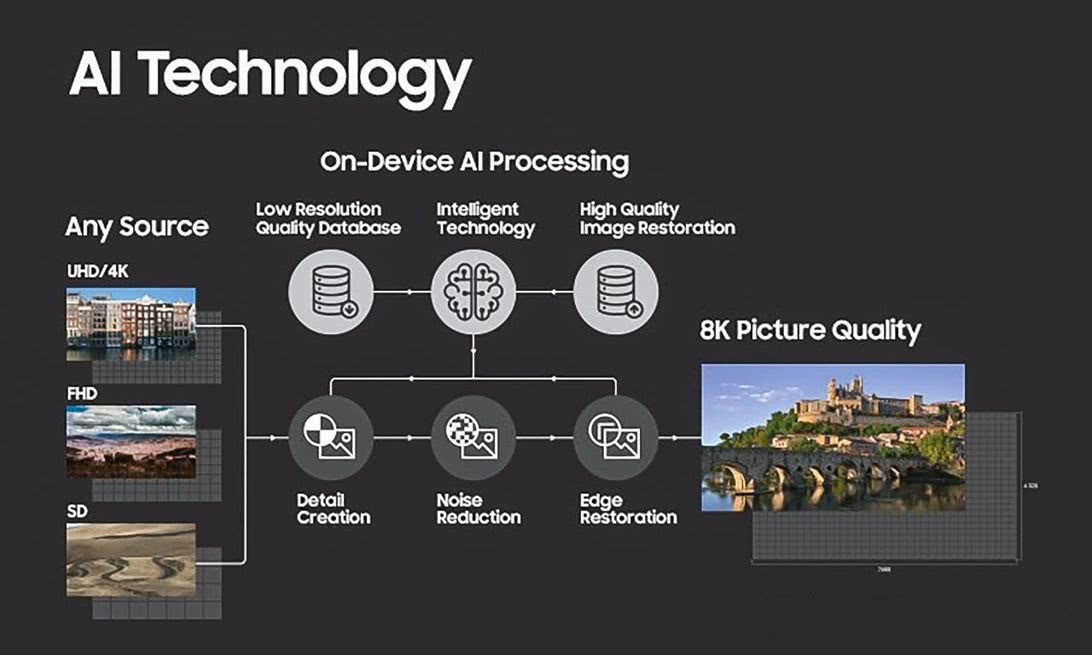
Here is a talk about artificial intelligence, and Samsung’s artificial intelligence upgrade mainly includes two aspects. The first is machine learning technology, video content, including a lot of video content analyzed by the computer. This creates new filters, which may include filters for football matches, filters for racing games, reality show filters, action movie filters, and drama-specific filters. For 1080p motion and 4K motion, it is even possible to provide different filters. Samsung said it has been able to offer ‘more than 100’ different filter options.
These filters are stored on each TV, and this leads to the second part of artificial intelligence technology. When you are looking at different content, the TV automatically analyzes the current image and determines what you are looking at. It then automatically applies the filters it determines to best suit the current content, providing a clearer picture.
Samsung is certainly not the only company to do so, although the Korean electronics giant seems to be the first company to combine these technologies in this particular way. For example, both LG and Sony have similar methods. LG’s AI ThinQ is a general term for integrating a variety of ‘artificial intelligence’ technologies, including speech recognition and voice control assistants. LG said it has studied more than 1 million items through a ‘deep learning’ algorithm. This allows the TV to analyze what the user is looking at and to choose the best overall settings for a particular content, which LG calls a deep learning screen. LG’s approach will also include consideration of indoor ambient light (artificial intelligence brightness), which is somewhat similar to most smartphones. But the TV will also analyze and adjust the effect of the sound based on the content. So in essence it sounds a bit like a more advanced, smarter automatic picture and sound mode.
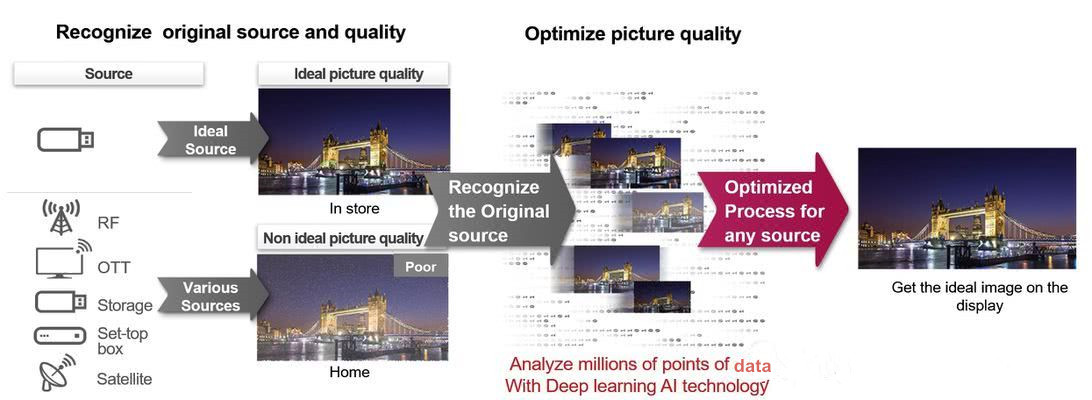
Although Sony does not call its technology ‘artificial intelligence,’ its 4K X-Reality Pro works similarly to Samsung’s artificial intelligence upgrade, using an extensive image database to automatically correct images. Sony’s terminology is ‘dual database processing.’ One database is used to determine which parts of the image need to reduce noise, while another database is used to determine which parts need to be enhanced .
If you want to learn more optical to electronic converting technology and application, please visit smartavlink.com
HD to 8K conversion requires a level of conversion pixel creation similar to that between DVD and HD. But if you start with high-definition content and add the most advanced processing features, an 8K TV should be able to present a better effect than we expected without 8K content. The combination of AI technology and photoelectric converting technology will become more and more popular in TV sets. The future TV is AI’s TV + Optical engine combined TV, which can bring us more high-definition visual effects.
